Introduction
Exosomes are membrane vesicles (30-100 nm in diameter) released from various cells and shown to function as transmitters of encapsulated nucleic acid (mRNA, microRNA) and proteins between remote cells. Their roles as a communication tool in cell-cell signal transduction and as a potential biomarkers for various diseases including cancer have recently been attracting research interest.1, 2) Accordingly, exosome research has been spreading across a wide variety of research areas in recent several years. Nevertheless, experimental techniques currently available for exosome research are still under development and many issues remain to be improved.
For example, among conventional techniques for exosome purification, ultracentrifugation and polymer precipitation (commercially available kits) have been shown to yield exosome preparations with large amounts of contaminants that seriously interfere with subsequent experiments. On the other hand, antibody-based affinity method and density gradient centrifugation are capable of purifying highly purified exosomes but are incapable of yielding intact exosomes, thus it is difficult to analyze their original physiological functions of exosomes.
Furthermore, Western Blotting and ELISA widely used for exosome detection have several disadvantages including the requirement of relatively large amounts of exosomes and difficulties in the detection of lowexpression marker proteins.
Accordingly, we have developed a new exosome analysis tool to resolve various problems in experimental techniques for exosome research as mentioned above. This new technique is described below. Data on isolation of high-purity extracellular vesicles using MagCaptureTM Exosome Isolation Kit PS are presented on pages 7-13, while data on high-sensitivity detection of extracellular vesicles using PS CaptureTM Exosome ELISA Kit PS are shown on page 16 and thereafter.
A new method for exosome purification using phosphatidylserine and Tim4
The exosome membrane contains proteins and lipids derived from secretory cells. Among those components, phosphatidylserine (PS) is known to be oriented inside the cell membrane of intact cells by the enzymatic activity of lipid flippase, and be known to be exposed also on the outer surface of exosome membrane.3) In addition, T-cell immunoglobulin domain and mucin domain-containing protein 4 (Tim4), the receptor involved in phagocytosis of apoptotic cells by macrophages, is known to bind PS via the IgV domain located within the extracellular region in a calcium ion-dependent manner.4)
Based on these findings, we developed a new and unprecedented method for exosome purification using Tim4-immobilized magnetic beads (capable of capturing exosomes in samples such as culture supernatants and serum in the presence of calcium ions and releasing them by elution with a buffer supplemented with a chelating reagent) in collaboration with Professor Rikinari Hanayama (Department of Immunology, Kanazawa University Graduate School of Medical Sciences) and successfully constructed an exosome purification kit based on these magnetic beads.5) This exosome purification kit, MagCaptureTM Exosome Isolation Kit PS, has realized easy purification of intact exosomes with higher purity than that obtained by any conventional methods for exosome purification. It is currently being established as a new exosome purification method replacing ultracentrifugation, the conventional gold standard.
References
- Tkach, M. et al. Communication by Extracellular Vesicles : Where We Are and Where We Need to Go. Cell 164, 1226-1232(2016).
- Raimondo, F. et al. Advances in membranous vesicle and exosome proteomics improving biological understanding and biomarker discovery. Proteomics 11, 709-720(2011).
- Trajkovic, K. et al. Ceramide triggers budding of exosome vesicles into multivesicular endosomes. Science 319(5867) : 1244-7(2008).
- Miyanishi, M. et al. Identification of Tim4 as a phosphatidylserine receptor. Nature 450, 435-439(2007).
- Nakai, W. et al. A novel affinity-based method for the isolation of highly purified extracellular vesicles. Sci. Rep. 6, 33935(2016).
A novel affinity-based method for phosphatidylserine (PS) on the surface of extracellular vesicles
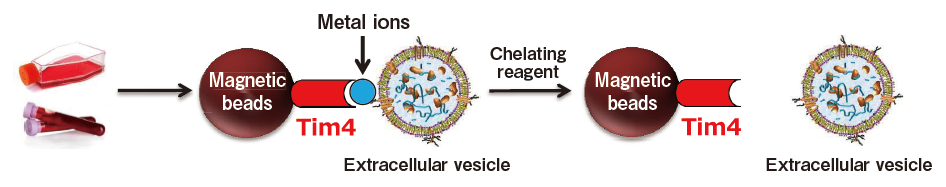
Extracellular vesicles are captured by phosphatidylserine (PS)-binding proteins and metal ions, then captured extracellular vesicles are eluted with a chelating reagent.
Comparison of capture ability between Tim4 and anti-exosomal marker antibody
Microplate wells, pre-coated with anti-CD antibodies (CD9, CD63, CD81) and Tim4 were incubated with nine types of pretreated ※ 1 cell culture supernatants. Captured exosomes on the plate were detected using biotinylated anti-CD antibodies (CD9, CD63, CD81).
※ 1 Pretreatment condition: 10,000 x g, 30 min.
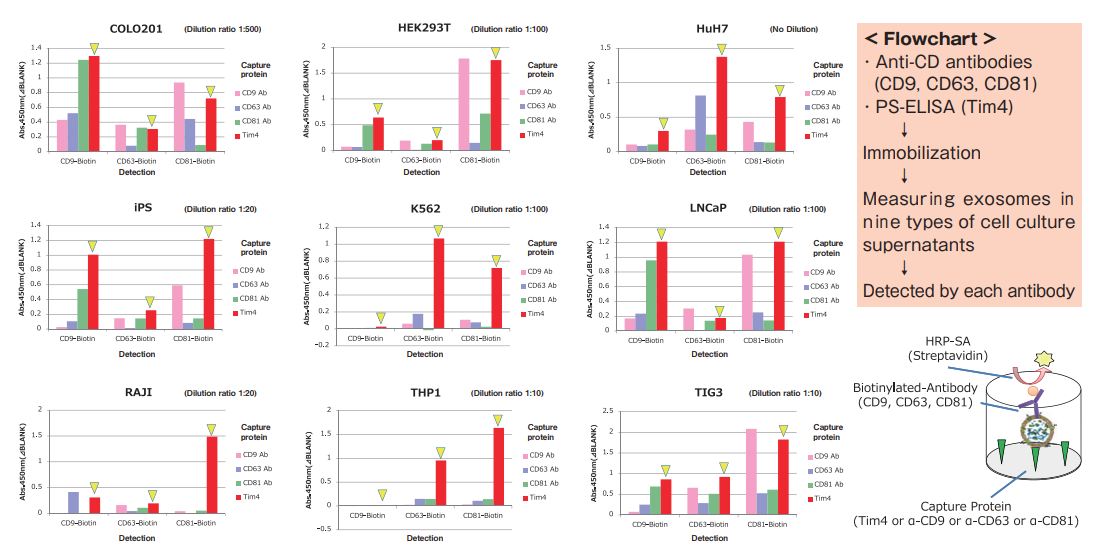
Compared with anti-exosomal marker antibodies, Tim4 was able to efficiently capture exosomes derived from a wide range of cell types.
Comparison of recovery efficiency with ultracentrifugation
From cell culture supernatant samples of various cell type and human serum samples obtained by centrifugation at 10,000 x g, exosomes were isolated and purified by PS affinity method and ultracentrifugation method. Then, purified exosomes were measured for signals of CD81 using PS Capture™ Exosome ELISA Kit. From absorbance of each sample, the amount of residual exosomes in a post-purification sample and the recovery rate of exosomes were determined for comparison.

The PS affinity method was found to be more efficient in recovering exosomes from various cell lines and serum than the ultracentrifugation method.
Application of the PS affinity method to ELISA
Introduction
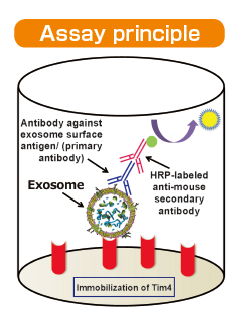
We developed PS Capture™ Exosome ELISA Kit by applying affinity binding of Tim4 protein with exosomes. This kit is capable of detecting exosomes at a sensitivity higher than that of conventional ELISA methods immobilization of antibodies against exosome surface markers. Exosomes in samples such as culture supernatants and serum are captured by Tim4 protein on adry plate in the presence of calcium ion. The captured exosomes are detected by a primary antibody against an exosome surface marker protein and a labeled secondary antibody. While a mouse anti-CD63 monoclonal antibody is provided with the kit, a user-provided mouse primary antibody against any other exosome surface marker may also be used for exosome detection.
The greatest feature of this kit is that it provides exosomes detection with higher sensitivity than that of Western Blot analysis and conventional product for exosome ELISA. First, the detection limit for exosomes in Western Blotting was examined for comparison with this kit (Figures 1a and b). Western Blot analysis of exosomes purified from COLO201 cells (of human colon adenocarcinoma origin) with an anti-CD63 monoclonal antibody detected exosomes in an amount as small as 75 ng on the protein basis. Next, the detection limits of this kit for exosomes purified from K562 cells (of human leukemia origin) and COLO201 cells were determined to be 49.9 pg and 10.9 pg, respectively, demonstrating that this kit had a detection sensitivity more than 1,000 times higher than that of Western Blotting (Figure 1c). Considering that the detection limits of conventional products for exosome ELISA range approximately several ng to several μg (refer to instruction manuals for individual products), the present results demonstrated that this kit utilizing affinity binding of exosomes to Tim4 via PS has a sensitivity more than 100 times higher than those of conventional ELISA methods involving immobilization of an antibody against an exosome surface protein marker.
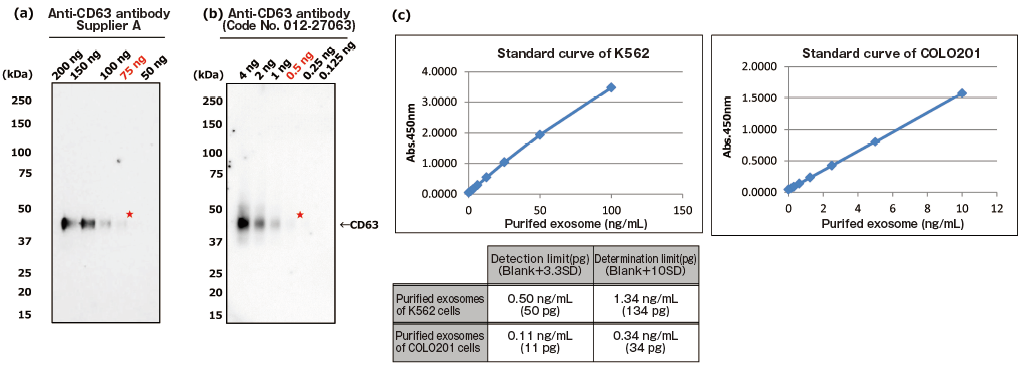
PS ELISA detected the marker proteins with 50-1,000 times higher sensitivity than WB.
| Fig. 1 Comparing the detection sensitivities of Western Blot and PS ELISA | ||
| (a), (b) Result of sensitivity by Western Blot with each of anti-CD63 antibody (supplier A and Wako: Code No. 012-27063). Sample: purified extracellular vesicles from cell culture supernatant of COLO201 cells with MagCaptureTM Exosome Isolation Kit PS (Code No. 293-77601) |
||
| ★:detection limit by Western Blot | ||
| (c) Result of limit by PS ELISA | ||
| A standard curve was prepared using blank value of buffer and absorbance value of 2-fold serial dilution samples of extracellular vesicles purified from cell culture supernatant of K562 cells and that of COLO201 cells with MagCapture™ Exosome Isolation Kit PS. Then, the detection limit of purified extracellular vesicles of K562 cells and COLO201 cells were calculated using its standard curve. (each dilution point: n=6, blank: n=12) | ||
